Path ID: DB09568_MESH_D015228_1
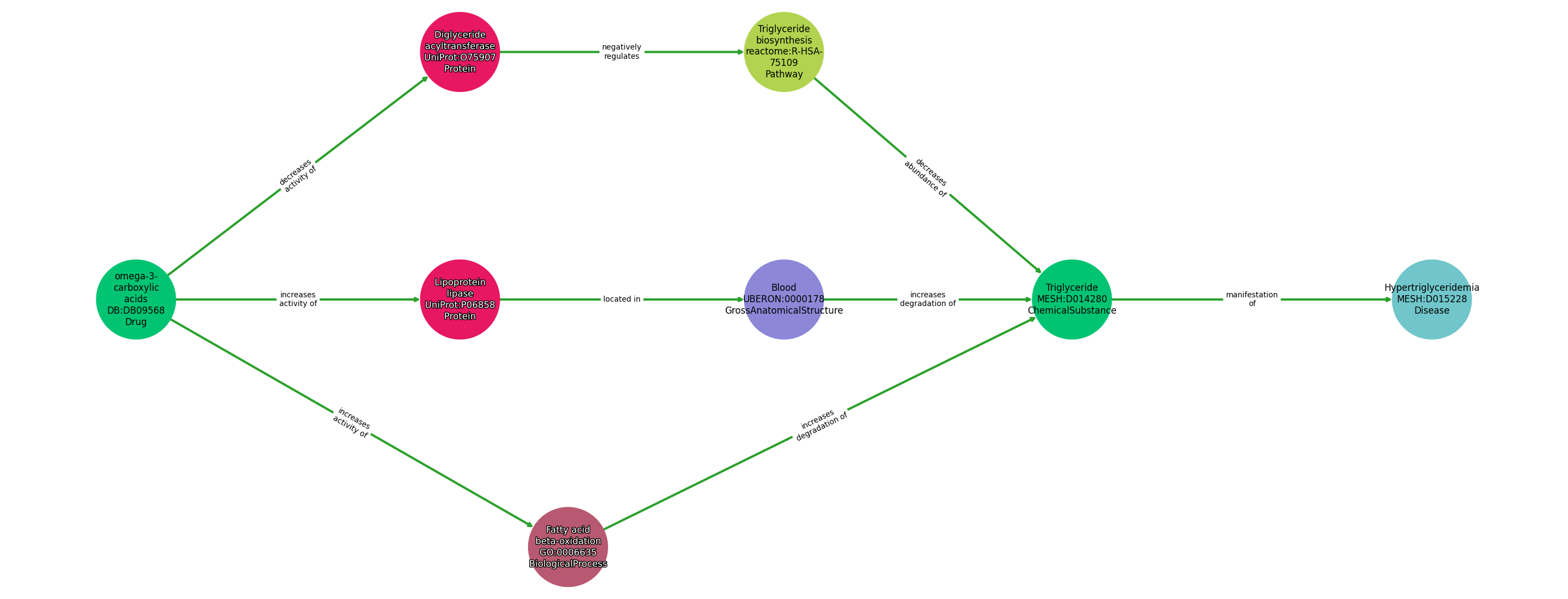
Concepts
| Identifier | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
| DB:DB09568 | omega-3-carboxylic acids | Drug |
| UniProt:O75907 | Diglyceride acyltransferase | Protein |
| reactome:R-HSA-75109 | Triglyceride biosynthesis | Pathway |
| GO:0006635 | Fatty acid beta-oxidation | BiologicalProcess |
| UBERON:0000178 | Blood | GrossAnatomicalStructure |
| UniProt:P06858 | Lipoprotein lipase | Protein |
| MESH:D014280 | Triglyceride | ChemicalSubstance |
| MESH:D015228 | Hypertriglyceridemia | Disease |
Relationships
NOTE: predicates are annotated in Biolink Model (v1.3.0)
| Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Omega-3-Carboxylic Acids | DECREASES ACTIVITY OF | Diglyceride Acyltransferase |
| Diglyceride Acyltransferase | NEGATIVELY REGULATES | Triglyceride Biosynthesis |
| Triglyceride Biosynthesis | DECREASES ABUNDANCE OF | Triglyceride |
| Omega-3-Carboxylic Acids | INCREASES ACTIVITY OF | Lipoprotein Lipase |
| Lipoprotein Lipase | LOCATED IN | Blood |
| Blood | INCREASES DEGRADATION OF | Triglyceride |
| Omega-3-Carboxylic Acids | INCREASES ACTIVITY OF | Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation |
| Fatty Acid Beta-Oxidation | INCREASES DEGRADATION OF | Triglyceride |
| Triglyceride | MANIFESTATION OF | Hypertriglyceridemia |
Comment: The main components of OM3-CA, eicosapentaenoic acid, and docosahexaenoic acid, are poor substrates for the enzymes responsible for the synthesis of triglycerides (TG). It enhances the clearance of TG from circulating VLDL particles; increased breakdown of fatty acids; inhibition of DAG; and increased activity of lipoprotein lipase in blood.
Reference: