Path ID: DB09230_MESH_D006973_1
Concepts
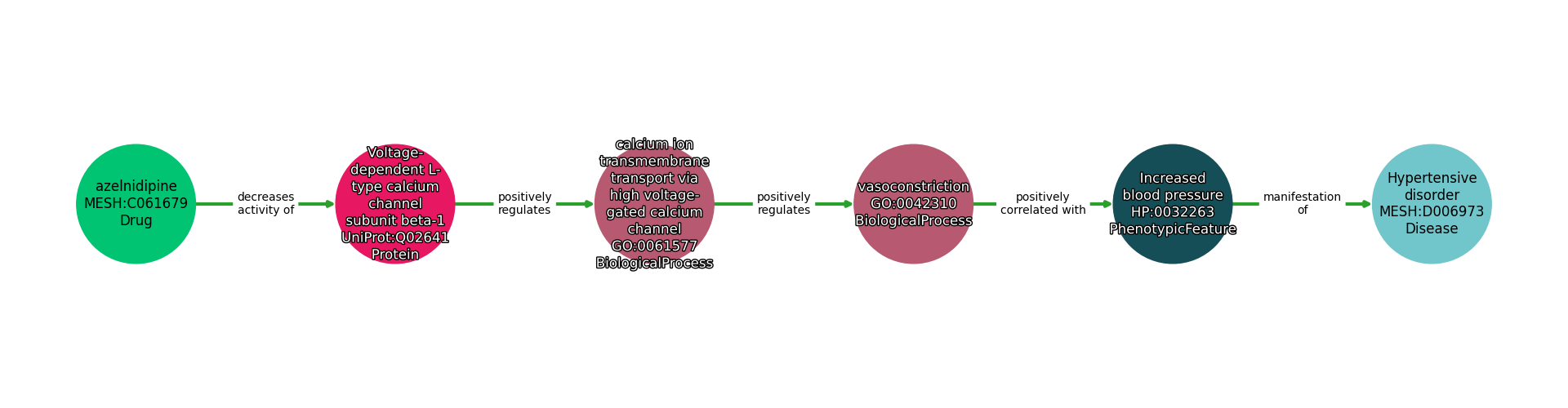
| Identifier | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
| MESH:C061679 | azelnidipine | Drug |
| UniProt:Q02641 | Voltage-dependent L-type calcium channel subunit beta-1 | Protein |
| GO:0061577 | calcium ion transmembrane transport via high voltage-gated calcium channel | BiologicalProcess |
| GO:0042310 | vasoconstriction | BiologicalProcess |
| HP:0032263 | Increased blood pressure | PhenotypicFeature |
| MESH:D006973 | Hypertensive disorder | Disease |
Relationships
NOTE: predicates are annotated in Biolink Model (v1.3.0)
| Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Azelnidipine | DECREASES ACTIVITY OF | Voltage-Dependent L-Type Calcium Channel Subunit Beta-1 |
| Voltage-Dependent L-Type Calcium Channel Subunit Beta-1 | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Calcium Ion Transmembrane Transport Via High Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel |
| Calcium Ion Transmembrane Transport Via High Voltage-Gated Calcium Channel | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Vasoconstriction |
| Vasoconstriction | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Increased Blood Pressure |
| Increased Blood Pressure | MANIFESTATION OF | Hypertensive Disorder |
Comment: The drug may also modulate other members of the Voltage-gated L-type calcium channel protein family (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/compound_report_card/CHEMBL1275868/) or T-type calcium channel protein family (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Azelnidipine).
Reference: