Path ID: DB09060_MESH_D059413_2
Concepts
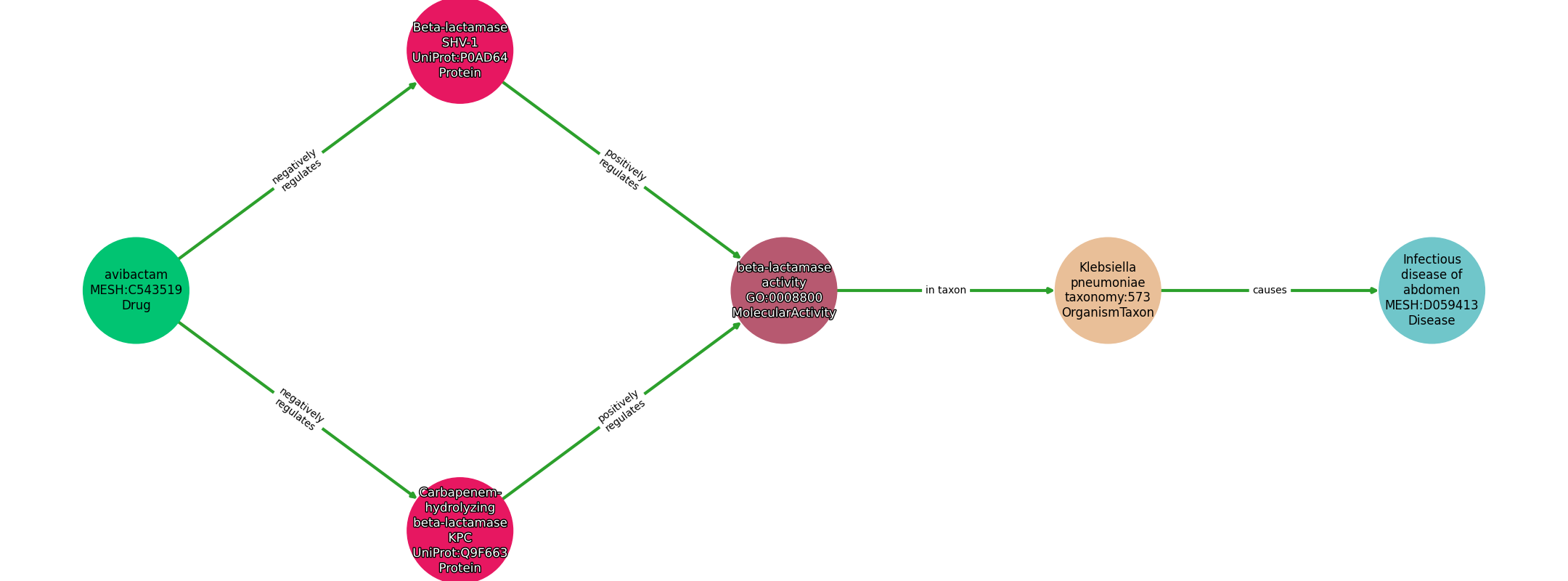
| Identifier | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
| MESH:C543519 | avibactam | Drug |
| UniProt:Q9F663 | Carbapenem-hydrolyzing beta-lactamase KPC | Protein |
| UniProt:P0AD64 | Beta-lactamase SHV-1 | Protein |
| GO:0008800 | beta-lactamase activity | MolecularActivity |
| taxonomy:573 | Klebsiella pneumoniae | OrganismTaxon |
| MESH:D059413 | Infectious disease of abdomen | Disease |
Relationships
NOTE: predicates are annotated in Biolink Model (v1.3.0)
| Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Avibactam | NEGATIVELY REGULATES | Beta-Lactamase Shv-1 |
| Avibactam | NEGATIVELY REGULATES | Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Beta-Lactamase Kpc |
| Beta-Lactamase Shv-1 | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Beta-Lactamase Activity |
| Carbapenem-Hydrolyzing Beta-Lactamase Kpc | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Beta-Lactamase Activity |
| Beta-Lactamase Activity | IN TAXON | Klebsiella Pneumoniae |
| Klebsiella Pneumoniae | CAUSES | Infectious Disease Of Abdomen |
Comment: This antibiotic inhbits beta-lactamases, enzymes that break antibiotics and therefore provide resistance to ampicillin and related beta-lacam antibiotics. Avibactam therefore is useful to treat infections caused by bacteria that are multi-resistant to β-lactam antibiotics.
Reference: