Path ID: DB06698_MESH_D008575_1
Concepts
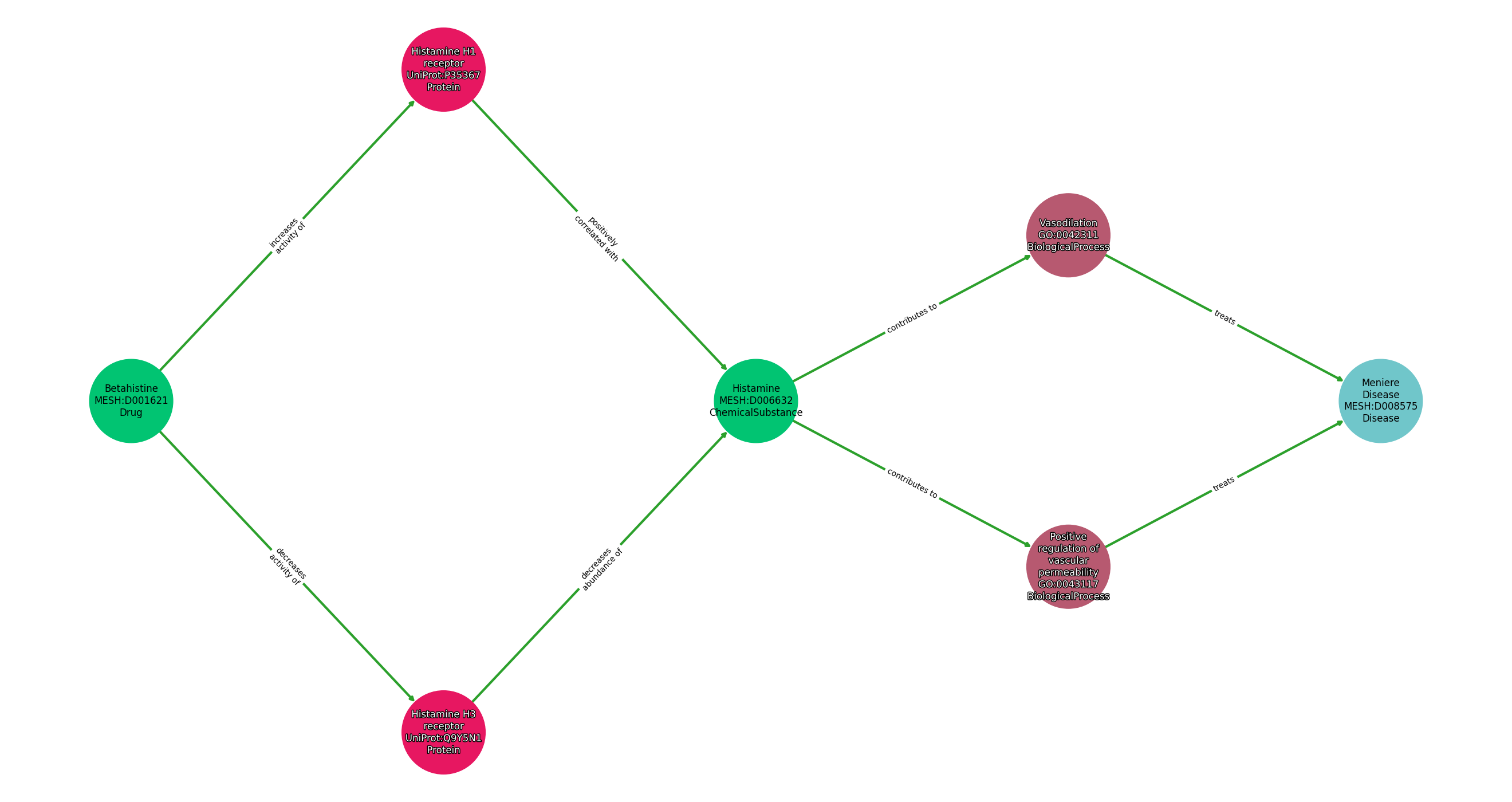
| Identifier | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
| MESH:D001621 | Betahistine | Drug |
| UniProt:P35367 | Histamine H1 receptor | Protein |
| MESH:D006632 | Histamine | ChemicalSubstance |
| GO:0042311 | Vasodilation | BiologicalProcess |
| GO:0043117 | Positive regulation of vascular permeability | BiologicalProcess |
| UniProt:Q9Y5N1 | Histamine H3 receptor | Protein |
| MESH:D008575 | Meniere Disease | Disease |
Relationships
NOTE: predicates are annotated in Biolink Model (v1.3.0)
| Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Betahistine | INCREASES ACTIVITY OF | Histamine H1 Receptor |
| Histamine H1 Receptor | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Histamine |
| Histamine | CONTRIBUTES TO | Vasodilation |
| Histamine | CONTRIBUTES TO | Positive Regulation Of Vascular Permeability |
| Betahistine | DECREASES ACTIVITY OF | Histamine H3 Receptor |
| Histamine H3 Receptor | DECREASES ABUNDANCE OF | Histamine |
| Vasodilation | TREATS | Meniere Disease |
| Positive Regulation Of Vascular Permeability | TREATS | Meniere Disease |
Comment: Betahistine was first approved by the FDA in the 1970s but withdrawn within approximately 5 years due to a lack of evidence supporting its efficacy.
Reference: