Path ID: DB01369_MESH_D013290_1
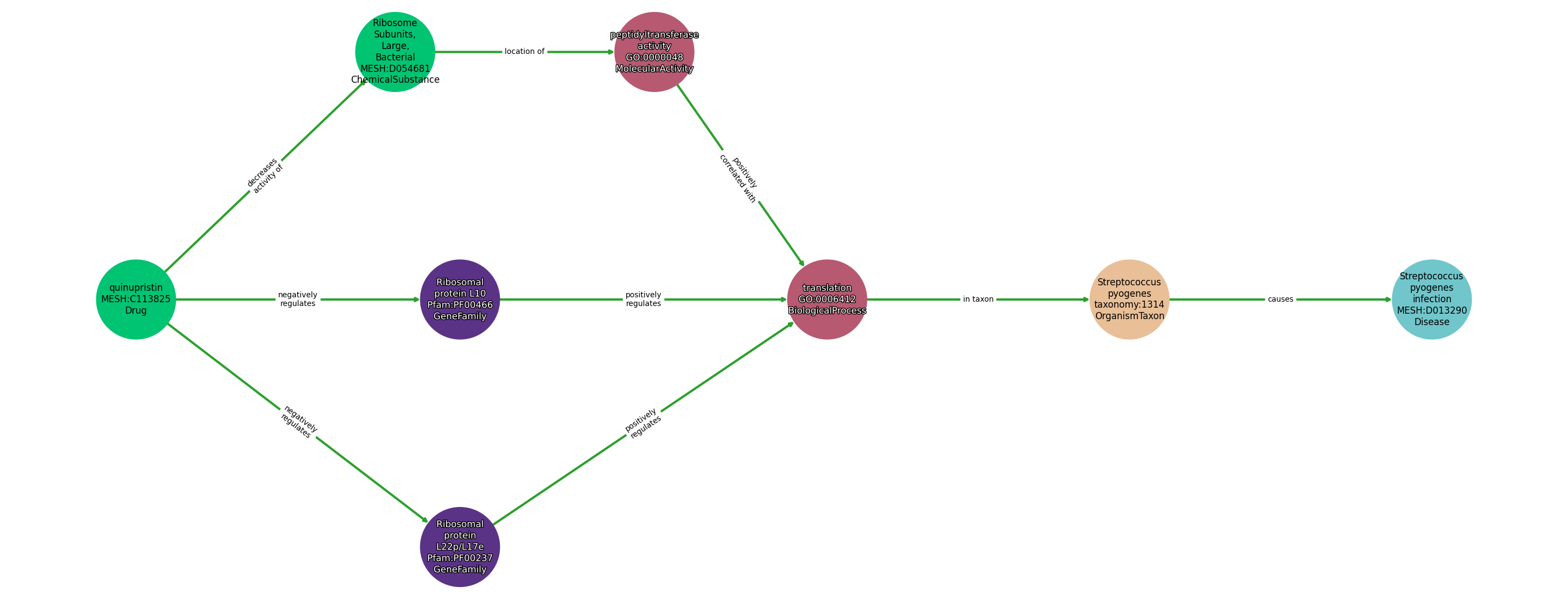
Concepts
| Identifier | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
| MESH:C113825 | quinupristin | Drug |
| MESH:D054681 | Ribosome Subunits, Large, Bacterial | ChemicalSubstance |
| GO:0006412 | translation | BiologicalProcess |
| GO:0000048 | peptidyltransferase activity | MolecularActivity |
| Pfam:PF00237 | Ribosomal protein L22p/L17e | GeneFamily |
| Pfam:PF00466 | Ribosomal protein L10 | GeneFamily |
| taxonomy:1314 | Streptococcus pyogenes | OrganismTaxon |
| MESH:D013290 | Streptococcus pyogenes infection | Disease |
Relationships
NOTE: predicates are annotated in Biolink Model (v1.3.0)
| Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Quinupristin | DECREASES ACTIVITY OF | Ribosome Subunits, Large, Bacterial |
| Quinupristin | NEGATIVELY REGULATES | Ribosomal Protein L10 |
| Quinupristin | NEGATIVELY REGULATES | Ribosomal Protein L22P/L17E |
| Ribosomal Protein L10 | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Translation |
| Ribosomal Protein L22P/L17E | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Translation |
| Ribosome Subunits, Large, Bacterial | LOCATION OF | Peptidyltransferase Activity |
| Peptidyltransferase Activity | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Translation |
| Translation | IN TAXON | Streptococcus Pyogenes |
| Streptococcus Pyogenes | CAUSES | Streptococcus Pyogenes Infection |
Comment: This drug is used in combination with dalfopristin. Both interfere with the bacterial protein synthesis, at different stages of the translation. Quinupristin inhibits the late phase of protein synthesis, whereas dalfopristin inhibits the early phase of protein synthesis in the bacterial ribosome. In combination, both drugs are more effective than each used individually (https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01369#description).
Reference: