Path ID: DB01238_MESH_D001321_1
Concepts
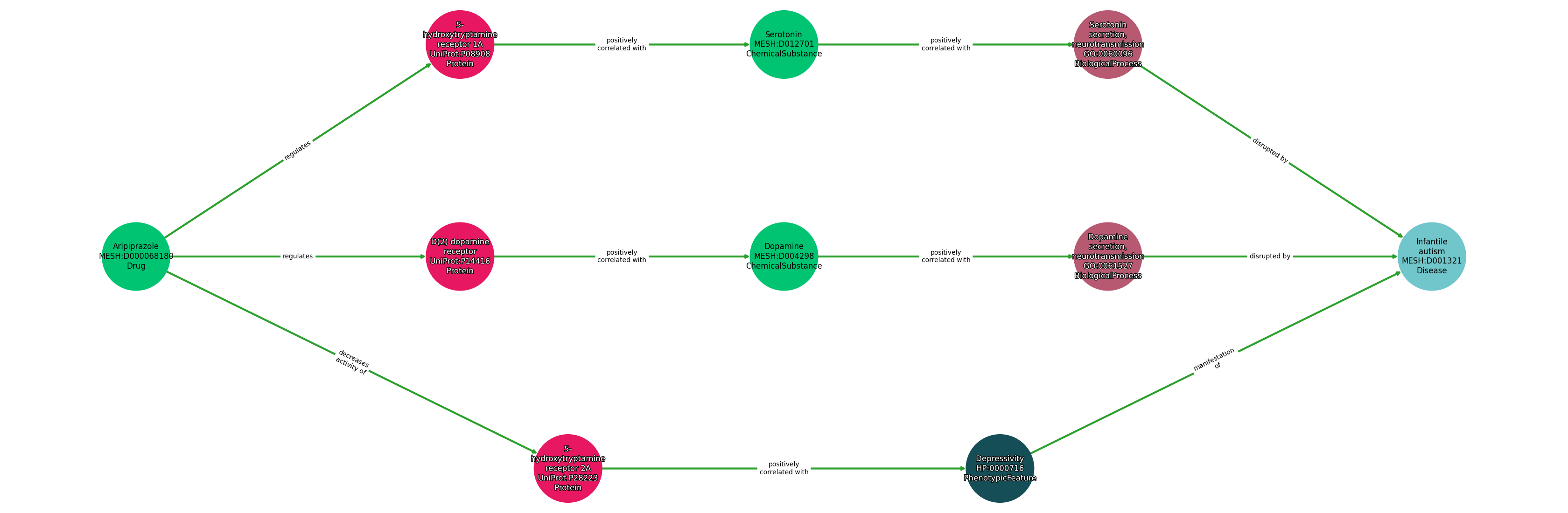
| Identifier | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
| MESH:D000068180 | Aripiprazole | Drug |
| UniProt:P14416 | D(2) dopamine receptor | Protein |
| UniProt:P28223 | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 2A | Protein |
| UniProt:P08908 | 5-hydroxytryptamine receptor 1A | Protein |
| MESH:D012701 | Serotonin | ChemicalSubstance |
| MESH:D004298 | Dopamine | ChemicalSubstance |
| HP:0000716 | Depressivity | PhenotypicFeature |
| GO:0060096 | Serotonin secretion, neurotransmission | BiologicalProcess |
| GO:0061527 | Dopamine secretion, neurotransmission | BiologicalProcess |
| MESH:D001321 | Infantile autism | Disease |
Relationships
NOTE: predicates are annotated in Biolink Model (v1.3.0)
| Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Aripiprazole | REGULATES | 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 1A |
| Aripiprazole | REGULATES | D(2) Dopamine Receptor |
| Aripiprazole | DECREASES ACTIVITY OF | 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 2A |
| 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 1A | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Serotonin |
| D(2) Dopamine Receptor | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Dopamine |
| 5-Hydroxytryptamine Receptor 2A | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Depressivity |
| Serotonin | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Serotonin Secretion, Neurotransmission |
| Dopamine | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Dopamine Secretion, Neurotransmission |
| Depressivity | MANIFESTATION OF | Infantile Autism |
| Serotonin Secretion, Neurotransmission | DISRUPTED BY | Infantile Autism |
| Dopamine Secretion, Neurotransmission | DISRUPTED BY | Infantile Autism |
Comment: The antipsychotic action of aripiprazole is likely due to the agonism of D2 and 5-HT1A receptors though the exact mechanism has not been defined.
Reference: