Path ID: DB01177_MESH_D015470_1
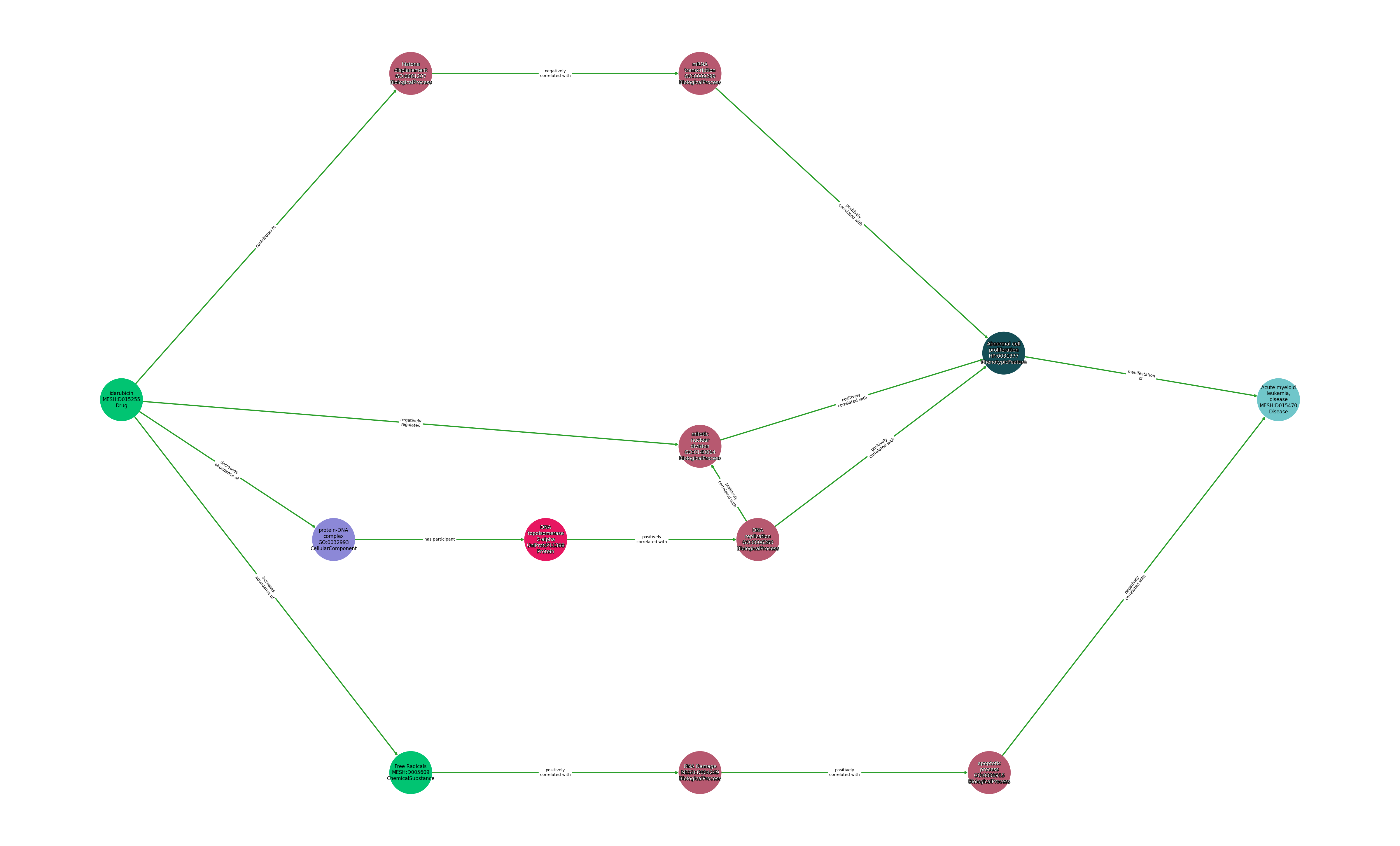
Concepts
| Identifier | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
| MESH:D015255 | idarubicin | Drug |
| GO:0001207 | histone displacement | BiologicalProcess |
| GO:0009299 | mRNA transcription | BiologicalProcess |
| UniProt:P11388 | DNA topoisomerase 2-alpha | Protein |
| GO:0032993 | protein-DNA complex | CellularComponent |
| MESH:D005609 | Free Radicals | ChemicalSubstance |
| MESH:D004249 | DNA Damage | BiologicalProcess |
| GO:0006260 | DNA replication | BiologicalProcess |
| HP:0031377 | Abnormal cell proliferation | PhenotypicFeature |
| GO:0006915 | apoptotic process | BiologicalProcess |
| GO:0140014 | mitotic nuclear division | BiologicalProcess |
| MESH:D015470 | Acute myeloid leukemia, disease | Disease |
Relationships
NOTE: predicates are annotated in Biolink Model (v1.3.0)
| Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Idarubicin | CONTRIBUTES TO | Histone Displacement |
| Histone Displacement | NEGATIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Mrna Transcription |
| Mrna Transcription | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Abnormal Cell Proliferation |
| Idarubicin | NEGATIVELY REGULATES | Mitotic Nuclear Division |
| Mitotic Nuclear Division | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Abnormal Cell Proliferation |
| Abnormal Cell Proliferation | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Disease |
| Idarubicin | DECREASES ABUNDANCE OF | Protein-Dna Complex |
| Protein-Dna Complex | HAS PARTICIPANT | Dna Topoisomerase 2-Alpha |
| Dna Topoisomerase 2-Alpha | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Dna Replication |
| Idarubicin | INCREASES ABUNDANCE OF | Free Radicals |
| Free Radicals | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Dna Damage |
| Dna Damage | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Apoptotic Process |
| Apoptotic Process | NEGATIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Disease |
| Dna Replication | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Abnormal Cell Proliferation |
| Dna Replication | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Mitotic Nuclear Division |
| Mitotic Nuclear Division | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Abnormal Cell Proliferation |
| Abnormal Cell Proliferation | MANIFESTATION OF | Acute Myeloid Leukemia, Disease |
Reference: