Path ID: DB00822_MESH_D000437_1
Concepts
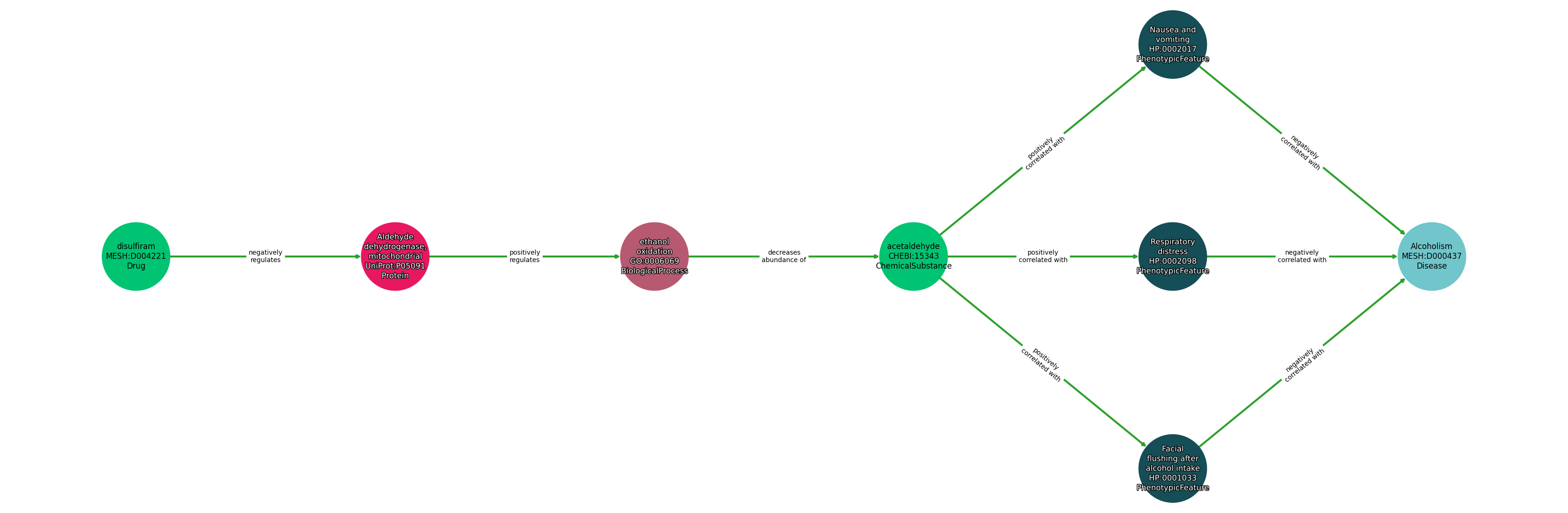
| Identifier | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
| MESH:D004221 | disulfiram | Drug |
| UniProt:P05091 | Aldehyde dehydrogenase, mitochondrial | Protein |
| CHEBI:15343 | acetaldehyde | ChemicalSubstance |
| GO:0006069 | ethanol oxidation | BiologicalProcess |
| HP:0001033 | Facial flushing after alcohol intake | PhenotypicFeature |
| HP:0002098 | Respiratory distress | PhenotypicFeature |
| HP:0002017 | Nausea and vomiting | PhenotypicFeature |
| MESH:D000437 | Alcoholism | Disease |
Relationships
NOTE: predicates are annotated in Biolink Model (v1.3.0)
| Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Disulfiram | NEGATIVELY REGULATES | Aldehyde Dehydrogenase, Mitochondrial |
| Aldehyde Dehydrogenase, Mitochondrial | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Ethanol Oxidation |
| Ethanol Oxidation | DECREASES ABUNDANCE OF | Acetaldehyde |
| Acetaldehyde | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Nausea And Vomiting |
| Acetaldehyde | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Respiratory Distress |
| Acetaldehyde | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Facial Flushing After Alcohol Intake |
| Acetaldehyde | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Respiratory Distress |
| Acetaldehyde | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Nausea And Vomiting |
| Facial Flushing After Alcohol Intake | NEGATIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Alcoholism |
| Respiratory Distress | NEGATIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Alcoholism |
| Nausea And Vomiting | NEGATIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Alcoholism |
Comment: Note that this drug is used as a support to the treatment of chronic alcoholism by producing an acute sensitivity to ethanol (as part of an avoidance therapy for alcohol abuse). It’s been suggested that disulfiram itself is unlikely responsible for the enzyme inactivation in vivo; several active metabolites of the drug, especially diethylthiomethylcarbamate, inhibits the enzyme in vitro (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/3117#section=Mechanism-of-Action).
Reference: