Path ID: DB00659_MESH_D000437_1
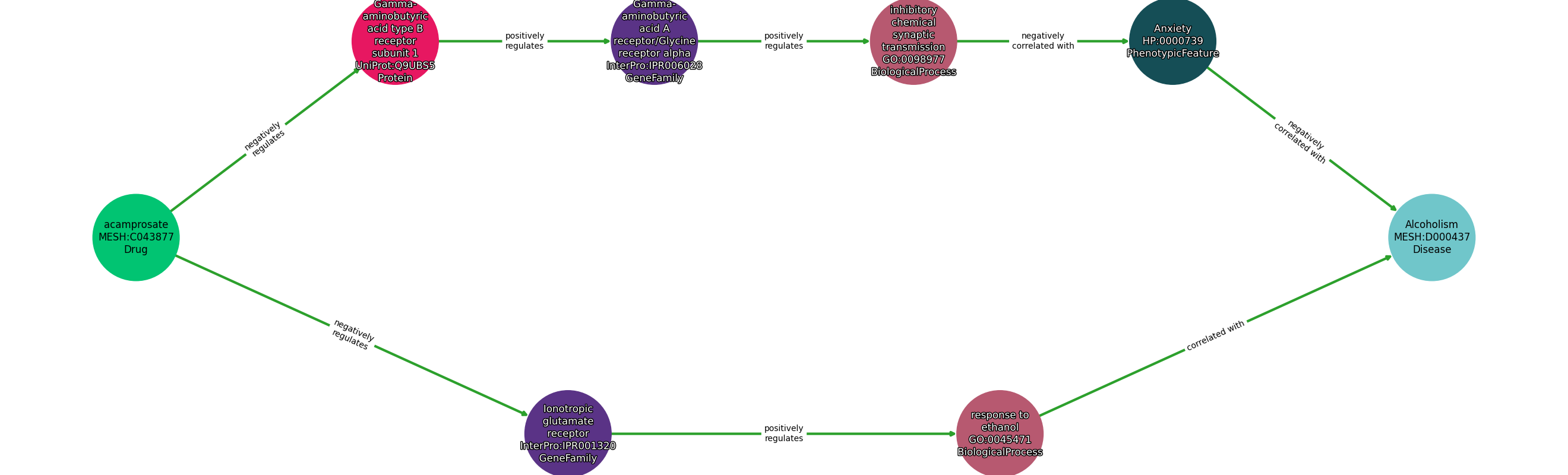
Concepts
| Identifier | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
| MESH:C043877 | acamprosate | Drug |
| InterPro:IPR001320 | Ionotropic glutamate receptor | GeneFamily |
| UniProt:Q9UBS5 | Gamma-aminobutyric acid type B receptor subunit 1 | Protein |
| InterPro:IPR006028 | Gamma-aminobutyric acid A receptor/Glycine receptor alpha | GeneFamily |
| GO:0045471 | response to ethanol | BiologicalProcess |
| GO:0098977 | inhibitory chemical synaptic transmission | BiologicalProcess |
| HP:0000739 | Anxiety | PhenotypicFeature |
| MESH:D000437 | Alcoholism | Disease |
Relationships
NOTE: predicates are annotated in Biolink Model (v1.3.0)
| Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Acamprosate | NEGATIVELY REGULATES | Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Type B Receptor Subunit 1 |
| Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid Type B Receptor Subunit 1 | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid A Receptor/Glycine Receptor Alpha |
| Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid A Receptor/Glycine Receptor Alpha | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Inhibitory Chemical Synaptic Transmission |
| Inhibitory Chemical Synaptic Transmission | NEGATIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Anxiety |
| Anxiety | NEGATIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Alcoholism |
| Acamprosate | NEGATIVELY REGULATES | Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor |
| Ionotropic Glutamate Receptor | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Response To Ethanol |
| Response To Ethanol | CORRELATED WITH | Alcoholism |
Comment: Chronic alcohol exposure is believed to alter the normal balance between neuronal excitation and inhibition. Both in vitro and in vivo studies seem to suggest acamprosate may interact with glutamate and GABA neurotransmitter systems centrally, and has led to the hypothesis that acamprosate restores this balance (https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/71158#section=Mechanism-of-Action). The drug may not an effective therapy if be used alone (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acamprosate#Pharmacodynamics). Acamprosate may influence GABAA transmission via inhibition of presynaptic γ-aminobutyric acid type B (GABAB) receptors (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/9514305/).
Reference:
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00659
- https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/compound_report_card/CHEMBL1201293/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acamprosate#Pharmacodynamics
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/GABAA_receptor#Structure_and_function
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Psychoactive_drug#Purposes
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/22346357/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23278595/