Path ID: DB00195_MESH_D006973_1
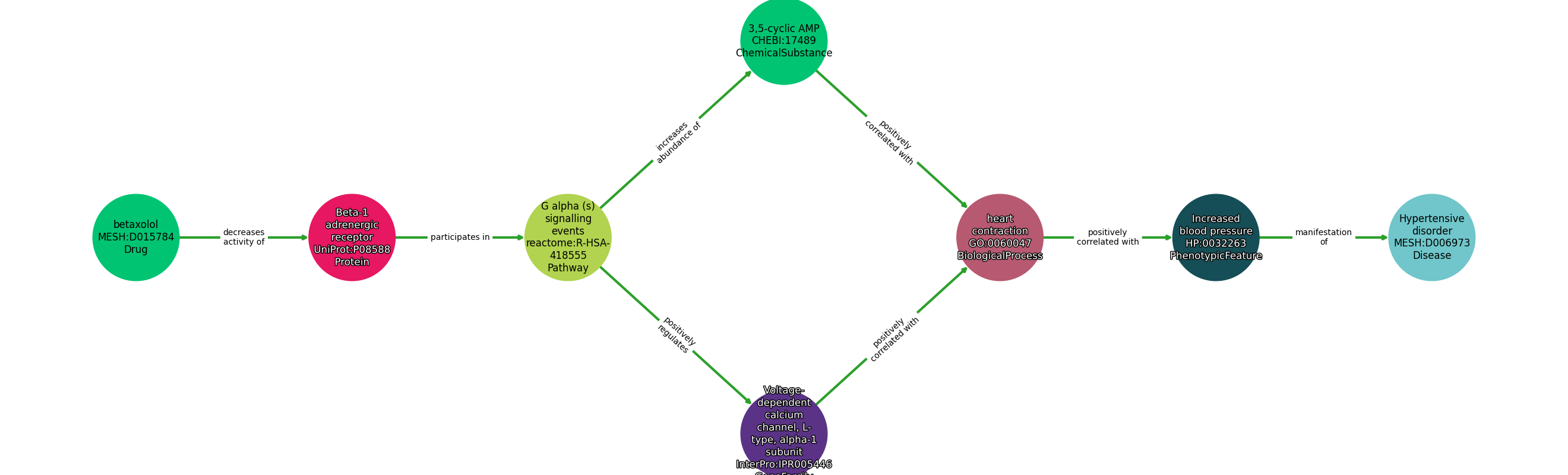
Concepts
| Identifier | Name | Type |
|---|---|---|
| MESH:D015784 | betaxolol | Drug |
| UniProt:P08588 | Beta-1 adrenergic receptor | Protein |
| reactome:R-HSA-418555 | G alpha (s) signalling events | Pathway |
| InterPro:IPR005446 | Voltage-dependent calcium channel, L-type, alpha-1 subunit | GeneFamily |
| CHEBI:17489 | 3,5-cyclic AMP | ChemicalSubstance |
| GO:0060047 | heart contraction | BiologicalProcess |
| HP:0032263 | Increased blood pressure | PhenotypicFeature |
| MESH:D006973 | Hypertensive disorder | Disease |
Relationships
NOTE: predicates are annotated in Biolink Model (v1.3.0)
| Subject | Predicate | Object |
|---|---|---|
| Betaxolol | DECREASES ACTIVITY OF | Beta-1 Adrenergic Receptor |
| Beta-1 Adrenergic Receptor | PARTICIPATES IN | G Alpha (S) Signalling Events |
| G Alpha (S) Signalling Events | INCREASES ABUNDANCE OF | 3,5-Cyclic Amp |
| G Alpha (S) Signalling Events | POSITIVELY REGULATES | Voltage-Dependent Calcium Channel, L-Type, Alpha-1 Subunit |
| Voltage-Dependent Calcium Channel, L-Type, Alpha-1 Subunit | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Heart Contraction |
| Heart Contraction | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Increased Blood Pressure |
| 3,5-Cyclic Amp | POSITIVELY CORRELATED WITH | Heart Contraction |
| Increased Blood Pressure | MANIFESTATION OF | Hypertensive Disorder |
Comment: L-type calcium channels are modulated by the adrenergic nervous system, hence betaxolol could indirectly modulate L calcium channels, decreasing heart rate and contraction, ultimately decreasing high blood pressure (https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/L-type_calcium_channel#Inhibition_and_modulation).
Reference:
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00195#mechanism-of-action
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Betaxolol
- https://www.ebi.ac.uk/chembl/compound_report_card/CHEMBL423/
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/2369#section=Pharmacology-and-Biochemistry
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/CAMP-dependent_pathway#Importance